A brachial plexus injury refers to an injury that occurs to the network of nerves connected to the spinal cord that sends signals to the shoulder, arm, and hand.
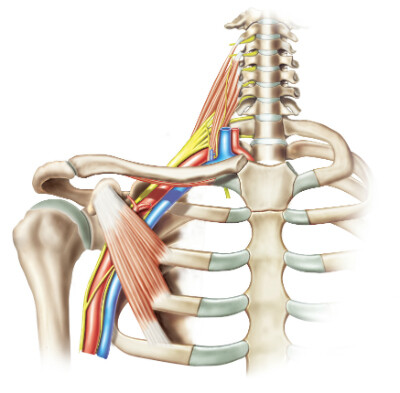
When a person suffers a brachial plexus injury in a St. Louis car accident, they may experience weakness in the arm, lack of muscle control, slow reflexes, and even paralysis. While many of these injuries can heal on their own, others may require splinting, physical therapy, and surgery.
Brachial Plexus Injuries
Nearly 1.2 percent of all adults have suffered a brachial plexus injury in their lifetime, and 89 percent of them are males. Almost 44-70 percent of these injuries are caused by motor vehicle accidents and workplace accidents.
Symptoms and Causes of Brachial Plexus Injuries
When the neck and arm are pulled way in opposite direction forcibly such as during car accident, the brachial plexus nerves can become stretched or torn. If the force is severe enough, it can pull the nerves away from the spinal cord. When a car accident victim suffers brachial plexus damage, they may experience symptoms such as:
- numbness, pain, and weakness in the arm, hand, and shoulder
- pins and needles sensation
- a burning sensation
- crushing pain
Traumatic brachial plexus injury can take many forms, and the most common of them is Erb’s Palsy, which affects the C5 and C6 nerves. It prevents the person from lifting their arm or flexing at the elbow. A brachial plexus injury can also affect the C8/T1 nerves, which can result in weakness and pain in hand. The most severe type results in complete paralysis of the arm.
Diagnosis and treatment of a Brachial Plexus injury
When a person suffers a suspected brachial plexus injury in a car accident, the doctor may order a CT myelography and MRT of the spine in order to determine whether nerves have detached from the spinal cord.
During the initial three months after the injury, the patient is usually observed for spontaneous recovery, because some patients gain function within this time period. The patient is generally prescribed pain medication and physical therapy during this period. If the patient shows no improvement during this period, the next step is usually surgery. Surgery is performed to repair elbow/shoulder weakness, nerve transfer, or complete brachial plexus reconstruction. Recovery even after surgery is often slow and uncertain. The patient needs physical therapy to restore the function and strength of the arm, hand, and shoulder.
Free Consultation with a St. Louis Car Accident Lawyer
Don’t talk to an insurance claims adjuster before speaking with The Hoffmann Law Firm, L.L.C. We can help you avoid making statements that may affect the outcome of your case. The consultation is free; you don’t pay unless we get you money!
Free Consultation (314) 361-4242